

The role of the occupational therapist in this phase includes: A fracture fixated with a plate or pins can move earlier if it is stable. no surgery) and/or how well the fracture has healed. It varies based on how the fracture is treated ( surgery vs. There is no specific time frame as to when this phase can be started. Instruction on active range of motion of the proximal and distal joints of the wrist, including the fingers, elbow, and shoulder.Enabling your return to light activities of daily living as allowed by your orthopaedist.Managing swelling with elevation, retrograde massage, and compression.Fabricating a custom-made orthosis (a support/bracing device) to immobilize the wrist while leaving the fingers free.The role of occupational therapy at this phase includes: This phase consists of stabilizing the fracture and enabling healing. Rehabilitation after a distal radius fracture consists of two phases.Ī volar wrist orthosis Phase 1-Immobilization If there are any complaints of numbness or tingling, a sensation test will also be completed.Īfter the initial assessment is completed, rehabilitation can begin.
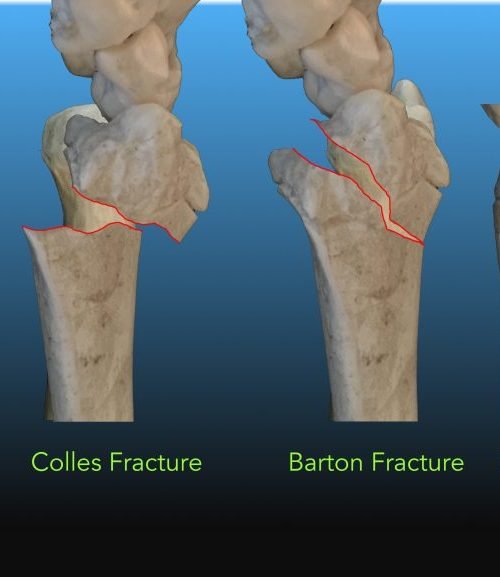
COLLES FRACTURE REHAB PROTOCOL FULL
Understanding what goals you have for returning to the activities and hobbies you enjoy-playing the piano, getting back on the tennis court, knitting, or other things that require a full return of flexibility, strength, and fine motor skills.This would include active range of motion (moving with no assistance), active assistive range of motion (movement requiring some help), and passive range of motion (movement guided completely by a therapist).

Discussing what type of range of motion you are cleared to perform by the orthopaedist.Clearing the shoulder and elbow to make sure there are no restrictions with motion or complaints of pain.Using a goniometer (an instrument for precisely measuring angles) to assess active range of motion of the wrist, forearm, and hand.Using a visual analog scale to assess pain.Using a tape measure to assess edema (swelling) in the wrist and hand.Reviewing the results of tests (x-rays, MRIs, CT scans) to understand if the fracture is healing, healed, or has a malunion (healed in a suboptimal position).Reviewing physician notes with you to understand where the fracture was located and how it was treated.Interviewing you to understand specific functional needs and problems performing activities of daily living, roles, and job requirements.The occupational therapist will perform an initial assessment, which will include: The decision of when you should start occupational therapy will be made by your treating orthopaedist. Your first visit with an occupational therapist could be right after surgery or after the cast is removed. This include opening a jar, buttoning a shirt, driving a car, caring for a child, as well as performing more specific functions for a job or sports activity. Physical therapy mainly treats your actual injuries or impairments-occupational therapy also treats impairments and additionally focuses on improving the ability to perform everyday tasks. While physical and occupational therapy are closely related, there is an important difference. Factors such as the severity of the injury, whether or not the dominant hand was injured, the availability of any assistance at home, the presence of comorbidities (two or more simultaneous conditions/impairments), and the job or role expectations the patient must meet all need to be taken into consideration when undergoing physical and/or occupational therapy.Īfter surgery/treatment of the injured wrist, your orthopaedist will prescribe some type of therapy program to get your wrist back to normal strength, flexibility, and function. However, the specific rehabilitation needs of a patient with a broken wrist can also vary widely. People of all ages can suffer a distal radius fracture (broken wrist) for a wide variety of reasons, from sports injuries on the field to falls and accidents at home.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
